GLD Network Dongle (Hardware Key) Troubleshooting
This information is directed towards IT
Managers/Network Administrators. As every network is different, these
suggestions are meant to help resolve issues but are not guaranteed to cover all
situations. Use caution making changes, especially when there are keys for
other products being used. Their requirements may be unique and could
interact with configurations for our key.
Note 1: Only the
commercial version of GLD is available for the network environment.
Note 2: Accessing a client machine (with GLD installed) via a remote desktop
session MAY NOT
WORK.
The HASP License Manager and DRM features of Windows will prevent this type
of
access. This
is NOT an issue with GLD. Network administrators might try a third
party
program like
VNC for configuration of remote clients.
Note 3: Network and standalone versions of GLD do
NOT coexist on the same network. If a
standalone
GLD key is installed on a network that is running network GLD, neither
version of
the software
will operate correctly. This is a limitation of the HASP licensing and
not a
problem with
GLD. Other HASP keys for different programs are not a problem and some
customers
have key servers with 6-10 HASP Keys installed and no issues.
SafeNet Network Dongle
The network dongle is manufactured by Gemalto/SafeNet. The company has changed hands a few times and will be referred to by numerous names including Aladdin, Sentinel, SafeNet or Gemalto. Their web site is at http://www.safenet-inc.com. The model number of the key commonly used in our network installations is HASP HL Net 10. The GLD2016 Network key is Red.
NOTE: In GLD network versions the key is RED. The pre-GLD2016 workstation key is PURPLE. In GLD2016 stand-alone key is BLACK
1: For troubleshooting purposes, you can load the GLD network
client on a workstation and test the network key by inserting the network key into
the workstation. This step will confirm that the key is programmed
correctly. If you cannot pass this step, you may have a blank key, a
key that is not authorized properly, or a key that has failed.
2: If you have confirmed that the key works correctly in a local
machine, you may move the key back to the key server. Launch GLD on
your network workstation and it should run properly. If it does not,
verify that both installations have the current SafeNet drivers. These
should automatically update and install but may be done manually by loading
the drivers. Run-time drivers may be found
here.
It is not necessary to install GLD on your key "server" installation and both the server and clients need to have these files.
When you install GLD on the workstation, the drivers are included with the
installation.
3: NOTE that the use of remote desktop for testing a GLD
installation remotely may fail. This is a DRM feature of Windows and
SafeNet that is intended to prevent this type of usage. Sometimes a
third party client such as VNC will provide an acceptable workaround but the
tools continue to evolve in ways that do not always make things easy for a
network administrator to test the remote installation. There is no
guarantee that the behavior of a workstation will appear the same when
accessed via RDT as opposed to sitting at the console of the workstation.
4: Use the web browser on the server and client workstation and use
the license manager admin to assist in your testing and configuration.
Type in the following URL :
http://localhost:1947
This is a powerful tool that will provide real-time feedback regarding the
key features, user sessions and traffic that has accessed your license key.
It will list all SafeNet keys on your server and allow you to identify the
specific key that you are using. You may blink the key to identify the
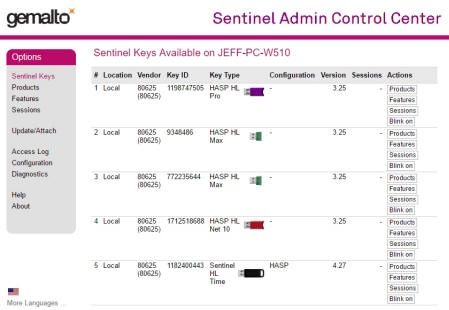
physical key presence. This feature is found at the top of the page in
the Key area. The example below shows a key server with multiple keys
and types installed:
Identify the Key:
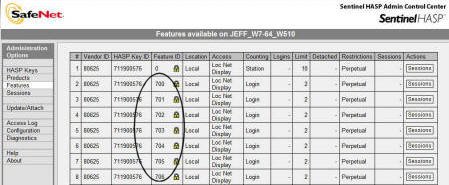
Verify Key is Programmed:
A key that is not properly programmed will show only the "0" feature ID or
no features at all. Below is an example of a programmed key.
Yours will look different depending on the version of software that was
purchased. Do not worry about these numbers unless asked by one of our
support staff. We can identify program versions and features from
these numbers.
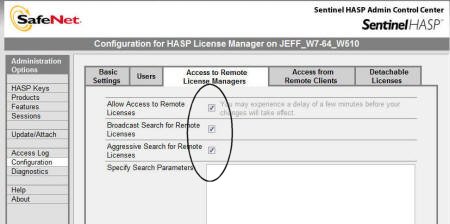
Configure the license manager for aggressive search:
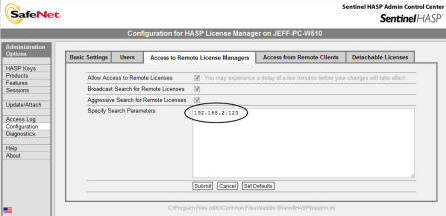
Multi-Locations: If you are trying to serve multiple subnets, each workstation may need to
have the server ip address specified in the search parameters box.
This should not be necessary if you are in the same subnet.
5: nethasp.ini files
Note that with modern OS there is NO need to use a nethasp.ini file and this
section is included primarily for a legacy (really old) installation and we
are not able to provide further support.
The presence of a nethasp.ini file will override the regular system drivers when it is present in the system due to a legacy installation,
other application that uses a key or mis-configured application. Try a search of the client system,
starting at the root, to locate a nethasp.ini file and if present, try renaming it with a .save extension so that it can be reused if necessary. With the system cleaned of the nethasp.ini file, attempt to discover the HASP license key. Use the license manager
http://localhost:1947 to monitor the detection. Use aggressive search as a next step. If still unsuccessful, return the nethasp.ini file or create a file in the GLD folder and explicitly point the file to the IP address of
your key server. Port 475 must be available for the license manager to communicate. You can temporarily turn off the firewall to minimize obstacles. If turning the firewall back on seems to disable the communication, add port 475 to udp and tcp. Ping the ip address of the key server to assure that communication exists through your network and subnets.
If you need to resort to the nethasp.ini, a sample below follows.
6: Sample nethasp.ini
file (for when standard configuration does not work):
The GLD key uses TCP/IP enabled, Broadcast using UDP.
7: Conflicting nethasp.ini files:
Several customers have found nethasp.ini files in core system directories - such as C:\Windows\System and C:\Windows\System32 - nethasp.ini files in this location will override any local settings that might be in place. We recommend only placing nethasp.ini files in the same directory as the applications if they are used - this prevents them from affecting other programs that use HASP devices - including our own. Any nethasp.ini files in common paths such as those listed above should be either renamed or removed.
8: The Safenet drivers and key are a product that GLD purchases for use from an outside vendor. We work with all of our customers to overcome any issues that are specific to their network environment. There are situations where the customer network is complicated to the point that we fall back to Gemalto/Safenet to help support their product. In the event that the customer network and configuration are preventing the Gemalto/Safenet system from working correctly, we will refer you directly to Gemalto/Safenet:
Gemalto / Safenet
Technical Support Website
Phone: 1-410-931-7520 International
email: support@safenet-inc.com
The Ground Loop Design vendor number for Safenet is: 80625
The Gemalto/Safenet product for network installations is: HASP HL Net 10
Further Questions? Contact our Support Department
